Software
We develop software packages, primarily for literature reviews. Our software is available in the CoLRev Environment and the fs-ise organization.
CoLRev

|
  |
CoLRev (Collaborative Literature Reviews) is an open-source environment for collaborative literature reviews. It integrates with different synthesis tools, takes care of the data, and facilitates Git-based collaboration. To accomplish these goals, CoLRev advances the design of review technology at the intersection of methods, design, cognition, and community building. The following features stand out:
- Supports all literature review steps: problem formulation, search, dedupe, (pre)screen, pdf retrieval and preparation, and synthesis
- An open and extensible environment based on shared data and process standards
- Builds on git and its transparent collaboration model for the entire literature review process
- Offers a self-explanatory, fault-tolerant, and configurable user workflow
- Operates a model for data quality, content curation, and reuse
- Enables typological and methodological pluralism throughout the process
SearchQuery
|
|
  |
SearchQuery is a Python package for parsing, validating, simplifying, and serializing search queries for academic databases. It currently supports PubMed, EBSCOHost, and Web of Science, using a standardized JSON schema (Haddaway et al., 2022).
- Programmatic use, CLI interface, and optional integration via pre-commit hooks
- Zero dependencies: easily embeddable across environments
- Extensible parser/validator architecture
- Tested on real-world queries from searchRxiv
BibDedupe

|
  |
BibDedupe is an open-source Python library for deduplication of bibliographic records, tailored for literature reviews. Unlike traditional deduplication methods, BibDedupe focuses on entity resolution, linking duplicate records instead of simply deleting them.
- Automated Duplicate Linking with Zero False Positives: BibDedupe automates the duplicate linking process with a focus on eliminating false positives.
- Preprocessing Approach: BibDedupe uses a preprocessing approach that reflects the unique error generation process in academic databases, such as author re-formatting, journal abbreviation or translations.
- Entity Resolution: BibDedupe does not simply delete duplicates, but it links duplicates to resolve the entity and integrates the data. This allows for validation, and undo operations.
- Programmatic Access: BibDedupe is designed for seamless integration into existing research workflows, providing programmatic access for easy incorporation into scripts and applications.
- Transparent and Reproducible Rules: BibDedupe’s blocking and matching rules are transparent and easily reproducible to promote reproducibility in deduplication processes.
- Continuous Benchmarking: Continuous integration tests running on GitHub Actions ensure ongoing benchmarking, maintaining the library’s reliability and performance across datasets.
- Efficient and Parallel Computation: BibDedupe implements computations efficiently and in parallel, using appropriate data structures and functions for optimal performance.
PRISMA Flow Diagram

|
 
|
PRISMA Flow Diagram is a Python package for creating PRISMA 2020–compliant flow diagrams programmatically. It is designed for transparency, sensible defaults, and layouts that adapt automatically to the structure and counts of a review.
The package supports:
- New systematic reviews (standard PRISMA 2020 flow)
- Updated reviews (previous + newly identified studies)
- Other search methods as an optional, structured extension
Users can either:
- Pass structured counts directly via a concise Python API, or
- Derive counts automatically from CoLRev
records.bibfiles, enabling seamless integration into review workflows.
Key features
- Validated PRISMA logic that prevents common reporting errors (e.g., screened ≤ identified − removed)
- Support for multi-lane PRISMA diagrams, including databases/registers and other search methods
- PNG output (with additional formats planned)
PRISMA Flow Diagram can be used standalone or as part of the CoLRev workflow, where it acts as a data package endpoint to generate PRISMA diagrams directly from review data. This ensures consistency between review data and the reported flow diagrams.
Deep-CENIC
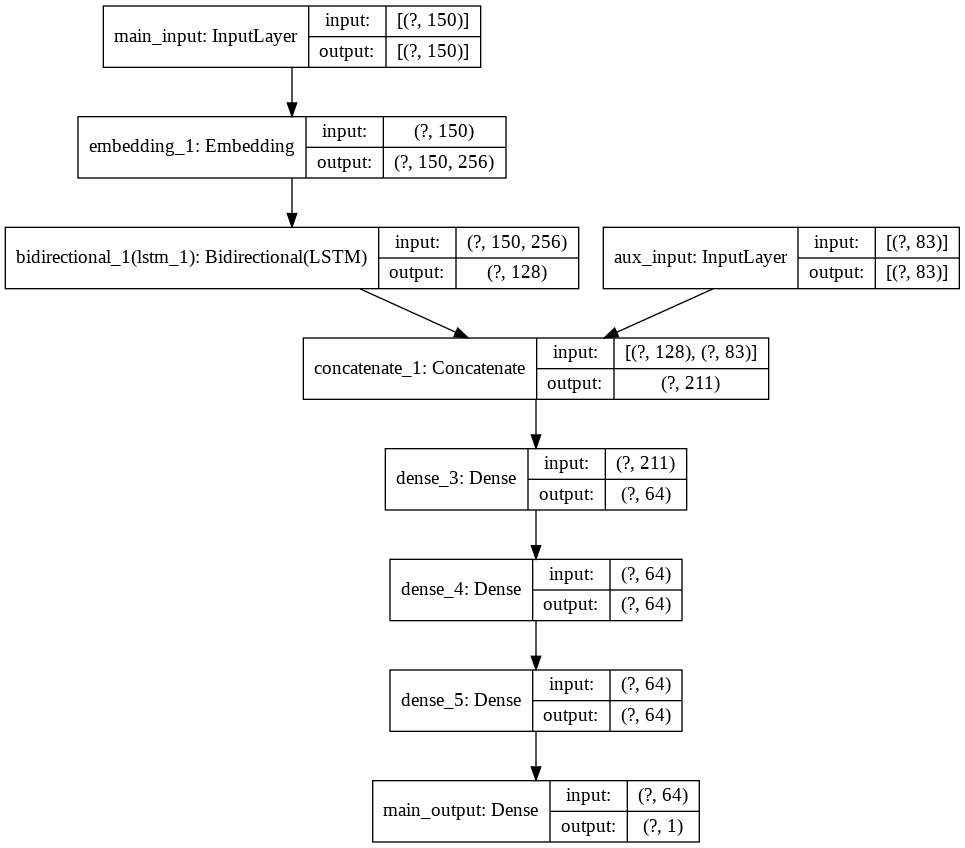
|
  
|
Deep-CENIC is a deep learning classifier that measures the ideational impact of Information Systems review articles.
Highlights
- Combines citation context, sentiment, position, and semantic similarity as predictive features
- Offers a gold-standard coded dataset for evaluating ML and DL models
- Reproducible pipeline using Docker and a Cookiecutter-like data structure
- Demonstrated in Decision Support Systems (scientometric and NLP evaluation)
- Includes transparent feature engineering for citation-based impact research
ENLIT
|
|
  
|
ENLIT supports scholars in exploring new literature by making backward searches more efficient and by guiding how to read a literature corpus.
What ENLIT does
- Extracts references from a literature corpus (set of PDFs) and compiles a deduplicated reference list
- Provides statistics on journals and authors that are frequently cited in the corpus
- Implements a novel exploratory reading strategy: first read the most influential papers, then skim the remaining ones
- Builds on GROBID for robust extraction of bibliographic information